Certain foods are so nutrient dense and have remarkable therapeutic qualities.
Introducing them into your diet can have a profound impact on your brain and overall health.
Today I’m going to share with you my three of my favourites.
When I started consuming these regularly, I saw improvements in my physical health, which moved the needle in the right direction towards optimal brain and mental health.
1. Turmeric (Curcumin)
Turmeric – the spice that gives curry its yellow colour – may be one of the most powerful foods.
For thousands of years, turmeric has been used medicinally in India. And now today, thousands of high-quality scientific studies have been published, looking into the hundreds of active compounds within turmeric that benefit the body and brain (24).
One of these compounds is curcumin.
Curcumin is the most heavily researched compound within turmeric.
It’s been shown to have a many medicinal properties, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
If you take a high-quality, concentrated source of curcumin, it is able to cross the blood-brain barrier and act as a neuroprotective agent, helping to prevent and treat a wide range of neurological and mental disorders.
A number of studies show that curcumin is a natural antidepressant, working significantly better than placebo and working just as well as Prozac in the treatment of “several mood-related symptoms” – but without the severe side effects that come along with medication.
Other research shows that curcumin is effective at fighting major depression by reducing stress hormones and increasing serotonin and dopamine, two neurotransmitters in the brain responsible for emotional wellbeing (26-30, 59-62).
Curcumin has also been shown to help people manage stress and anxiety and overcome trauma. In one study, the curcumin reduced "stress-related depressive symptoms" in animals exposed to chronic stress. In other words, it made them more resilient (31).
And a ground-breaking 2015 study demonstrated that curcumin can prevent new traumatic memories from being stored in the brain, and can remove “fear memories” already existing in the brain. The researchers suggested that curcumin should be seriously considered as a treatment for post-traumatic stress disorder (32).
“This suggests that people suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder and other psychological disorders that are characterized by fearful memories may benefit substantially from curcumin.”
Lastly, curcumin powerfully protects the aging brain, improves attention and memory in older individuals, and prevents and delays the development of Alzheimer’s.
In fact, seniors in India who eat turmeric regularly have the lowest rate of rate of Alzheimer’s in the world (33, 34, 58, 66).
How Can A Spice Possibly Treat Mental Illness?
Almost every chronic disease – including depression, anxiety, PTSD and Alzheimer’s – has been linked to chronic, low-level inflammation. People with clinical depression in particular have been shown to have 30 percent more brain inflammation than the general population (35-38).
And curcumin has potent anti-inflammatory effects. Many researchers point to this as the main reason why the compound is so beneficial for people suffering from these diseases (39- 45).
“Despite what has been previously believed, depression is not all about brain chemicals such as serotonin. Our findings support consistent research that depression is associated with increased inflammation and oxidative stress and it can be treated with an agent that has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. There is now increasing support for the antidepressant effects of curcumin, with a previous study demonstrating curcumin to be as effective as a pharmaceutical antidepressant for the treatment of depression.”
Curcumin also increases the amount of omega-3 fatty acids in the brain. It does this by increasing enzymes that enhance the synthesis of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) from its precursor alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (56).
And as I’ve discussed before, ALA is usually poorly converted into DHA, and DHA deficiency is linked to several brain and mental health disorders. So taking both krill oil and curcumin can support the fatty acid composition of your brain.
Another possible explanation is that curcumin boosts Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), a protein in the brain that increases the growth of new brain cells, and is linked to improved brain function and a lower risk of mental disease. It's been shown that people with depression and Alzheimer’s have reduced levels of BNDF in their brain (46-50, 31).
Curcumin definitely helped me overcome post-concussion syndrome, and this makes sense considering the research showing that it counteracts cognitive impairment caused by traumatic brain injury. It can also delay and even reverse general deterioration of cognitive function, and may even improve memory and make you smarter (51, 52, 57).
But before you go and start eating lots of turmeric and curcumin, it’s important to know how to take it and in what form.
The Best Form of Curcumin For Your Brain
It is difficult to experience the full therapeutic effects of curcumin by simply eating turmeric. This is because the curcumin content of turmeric is low - only about 3% of turmeric is made up of curcumin (52).
Most of the studies I have referenced use turmeric extracts that contain large amounts of curcumin – more than what you’d be able to consume simply by adding turmeric to your meals. On top of this, curcumin is very inefficient at absorbing into the bloodstream and reaching the brain. Luckily, science and technology has been able to concentrate significant amounts of curcumin into supplement form and increase its bioavailability (54, 55).
There are several different patented forms of “bioavailable” curcumin and I’ve tried most of them. But I didn’t notice a significant effect from most of them, making me think that they are not actually “bioavailable”, or at the very least, they aren’t able to cross the blood-brain barrier effectively and reach the brain.
But I did notice a difference from this form of curcumin.
Based on my experience and research, it is the most effective form of curcumin for the treatment of brain and mental disorders, as it’s formulated in a way that enables the active ingredients to cross the blood-brain barrier. Other “bioavailable” forms of curcumin will likely still affect the rest of the body, but not the brain.
That’s why I recommend it. It is one of my favourite supplements and since it is a fat soluble, I take it every day with a fatty meal.
2. Coconut Oil (MCTs and Ketones)
Coconuts are largely made up of saturated fat, and since the 1950s, there has been a war on saturated fat (5).
As a result, coconut oil has been vilified and blamed for clogging arteries and causing heart disease.
But, as I’ve discussed before, saturated fat is actually harmless. It appears to be “common knowledge” that it's bad for us and should be avoided, but this is a myth that has been disproven over and over (3, 4, 6, 7).
In fact, when people make coconut a big part of their diet, they have lower rates of heart disease, stroke and other chronic diseases (1, 2, 9).
And fats, particularly the ones from coconut oil, are crucial for optimal brain and mental health. The brain is 60% fat and the integrity of your brain cell membranes depend on high-quality dietary fat (8).
“ The low-fat approach to eating hasn’t helped us control weight or become healthier. Detailed research — much of it done at Harvard — shows that the total amount of fat in the diet isn’t really linked with weight or disease.”
I used to eat coconut oil every day. But I actually don’t eat as much anymore because I got sick of its taste. Knowing it was healthy for me, I actually ate way too much that I actually started to despise the taste of coconut.
But coconut oil also contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCT). MCTs are fatty acids of a smaller length that are easily digested in the body, and quickly metabolized into ketones by the liver. Ketones are an alternative source of fuel, which can quickly recharge the brain’s malfunctioning cells and improve cognitive function in susceptible individuals. The ketones that result from supplementing with pure MCT oil readily cross the blood-brain barrier and provides instant energy to brain cells (10, 21).
I used to supplement with 1-2 tablespoons of pure MCT oil every morning.
I now take an exogenous ketone supplement that quickly puts me into a ketogenic state and immediately increases my mental clarity. It works better than coconut oil and MCT oil, and it gives my brain a steady supply of ketones and energy to start my day.
Research is accumulating in support of ketones, coconut oil and its MCTs.
Researchers have labelled coconut oil an “anti-stress and antidepressant nutritional oil” after finding that it can reduce stress and depression by increasing antioxidants in the brain (11).
And high-fat diets and ketones can help slow down aging in the brain by repairing cell damage, which can help treat memory loss, dementia, mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, stroke, epilepsy and traumatic brain injury (12, 16-20).
And you don’t have to wait days or months to witness the neuroprotective benefits.
One study in the journal Neurobiology of Aging showed significant cognitive and memory improvements within 90 minutes of taking MCT oil (13).
It’s quite possible that these brain and mental health benefits may stem from ketone production, the MCTs within coconut oil, and/or coconut oil’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (14, 15).
Bacteria, viruses, inflammation and our immune system also impact the health of our brains, and lauric acid, one of the saturated fatty acids found in coconut oil, has antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, and immune-boosting properties (22).
Caprylic acid, another main fatty acid in coconut oil and MCT oil, improves circulation, has anti-aging properties and can help treat Alzheimer's (23).
And you don’t need to stick with coconut oil.
Coconut milk, water and meat are other ways to get the benefits of coconut and MCT oil.
Or you can simply take ketones to experience the fastest and most powerful beneficial effects.
3. Organ Meats (Beef Liver)
You’re going to eat my what?
Organ meats are nutritional powerhouses.
Traditional cultures recognized this and have consumed them for thousands of years.
Unfortunately, we hardly we eat them today.
In some traditional cultures, they only ate the organ meats. They threw away muscle meat or gave it to the dogs. And that's obviously the opposite of what we do today. The thought of throwing away a lean piece of steak to your dog seem insane. But muscle meat just isn't as nutritious as the rest of the animal.
And if you look at predatory animals, after they kill their prey, they instinctively start eating the organs first, saving the muscle meat for later.
In one of my favourite books called Deep Nutrition: Why Your Genes Need Traditional Food, Dr. Catherine Shanahan recommends the consumption of organ meats for optimal gene function.
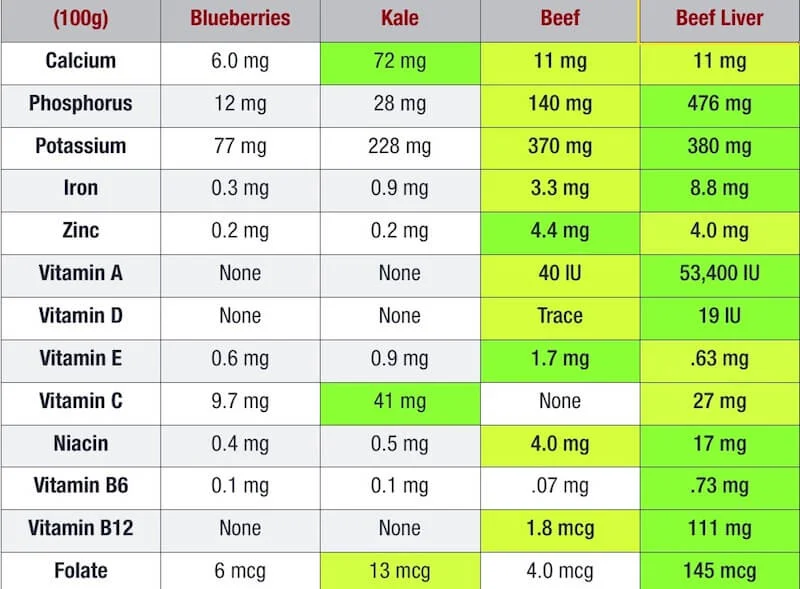
Beef liver in particular is incredibly nutrient dense. It’s nature multivitamin, containing more nutrients, gram for gram, than any other food. It’s actually a superfood. And I don’t like using the word "superfood". But beef liver actually fits the definition of a superfood, especially if it’s coming from grass-fed cows.
We hear over and over that fruits and vegetables are so nutritious. And they are. They should definitely make up a large part of your diet, as they include higher amounts of phytonutrients compared to animal foods. But when it comes to vitamins and minerals, fruit and veggies pale in comparison to organ meats such as liver.
Liver has almost everything in it that you need for optimal brain and mental health (63):
An excellent source of high-quality protein and amino acids
Vitamin C
Minerals such as zinc, potassium, magnesium, phosphorous, manganese, iron and chromium, some of which are very important for cognitive function and overall brain health.
Fat soluble vitamins A, D, E, K. Liver is the most concentrated source of retinol (preformed vitamin A) found in nature.
All of the B vitamins, including choline, B12 and folate, which support methylation, a biochemical process that is very important for robust and vibrant brain and mental health. Liver has 17 times more vitamin B12 than regular ground beef (64).
That’s why I recommend people throw away their multivitamin and eat liver instead. The great thing about organ meats such as liver is that they're much cheaper than muscle meat. So you actually save money by purchasing the healthiest part of the animal.
And if you can’t find high-quality grass-fed liver in your area or don’t like the taste of liver, I recommend raw beef liver powder in capsule form. I can’t stand the taste of liver, so I take 4 capsules every day.
Some people object to eating liver, as they believe the liver filters and stores toxins in the body. But the liver doesn't store toxins. It neutralizes them, and then they are flushed out of the body. Toxins that the body can't eliminate often accumulate in the fat of the animal, not the liver. That's why I recommend eating lean meats if you aren't eating organic, grass-fed meats. You don't really want to be eating the fat (or organs) of sick, conventional animals.
Another objection is that it contains animal fat and cholesterol. But as I've discussed before, saturated fat and cholesterol are not bad for your health. This is a huge myth.
Other than liver, you can also try incorporating other organs into your diet, including beef kidney, tongue, heart and even brain into your diet.
That's right, brain.
Some traditional cultures believe “like supports like” and eating the organs of a healthy animals supports the organs of the eater. So it’s possible that eating the brains of healthy animals could support the health of your own brain. And this would make sense since cow brain is full of healthy omega-3 fats and B12, which help fight depression, fatigue and cognitive decline.
Conclusion
Nutrient-based medical treatments used to be the norm.
Unfortunately, the general public is now convinced that pharmaceutical medicine is their only option.
But it’s not.
Food-based interventions work and they helped me get better.
And despite all the research demonstrating the powerful medicinal properties of these foods, the pharmaceutical industry and conventional medicine seem to ignore them.
They’re found in millions of kitchens around the world, so they lack exclusivity and therefore profitability.
They threaten the status quo and pharmaceutical industry revenue.
Unless they can be transformed into patented substances, the pharmaceutical industry doesn’t have a financial incentive to research and promote them to physicians.
Unless an investor is willing to pay millions of dollars upfront to pay for multi-phased, double-blind, randomized control trials, they will never be approved for clinical practice and prescribed by your doctor.
You don’t have to wait around for all of this to happen.
You can take control of your own brain health and try them yourself:
Coconut oil, MCT oil and/or ketones
Grass-fed beef liver or desiccated liver supplements
References:
(1) http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/34/8/1552.short
(2) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8450295
(3) http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/early/2010/01/13/ajcn.2009.27725.abstract
(4) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3519928
(5) http://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/fats-and-oils/508/2
(7) http://www.ajcn.org/cgi/content/abstract/ajcn.2009.27725v1
(8) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20329590
(9) http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/early/2010/01/13/ajcn.2009.27725.abstract
(10) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2604900/
(11) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4247320/
(12) http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/11/141105112614.htm
(13) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15123336
(14) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24613207
(15) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20645831
(16) http://wwwhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2367001/ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2367001/
(17) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24150106
(18) http://www.scienchttp://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1933721308000937direct.com/science/article/pii/S1933721308000937
(19) http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/pdf/1743-7075-6-31.pdf
(20) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1474442208700929
(21) http://www.nutritionjrnl.com/article/S0899-9007(12)00365-6/abstract
(22) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC444260/pdf/aac00361-0029.pdf
(23) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21830350
(24) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3633300/
(25) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23832433
(26) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23832433
(27) http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00213-008-1300-y
(28) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014299905006230
(29) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19882093
(30) http://www.jad-journal.com/article/S0165-0327(14)00362-0/abstract
(31) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006899306027144
(32) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25430781
(34) http://www.drweil.com/drw/u/ART03064/Alzheimers-Disease.html
(35) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12490960
(36) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12490959
(37) http://www.jci.org/articles/view/57132
(38) http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/01/150128113824.htm
(39) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19594223
(40) http://www.jbc.org/content/270/42/24995.full
(41) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17885582
(42) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12676044
(43) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304383501006553
(44) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1357272508002550
(45) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15489888
(46) http://www.hindawi.com/journals/tswj/2009/624894/abs/
(47) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2504526/
(48) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006322303001811
(49) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0896627391902733
(50) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166432812006997
(51) http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0031211
(52) http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10522-013-9422-y
(53) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17044766
(54) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3918523/
(55) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3918227/
(56) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25550171
(57) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16364299
(58) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25277322
(59) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=curcumin%205-ht2c
(60) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17022948
(61) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26610378
(62) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16171853
(63) http://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/beef-products/3469/2
(64) https://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/search/list
(65) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781139/