I used to suffer from massive brain fog, especially after I suffered multiple concussions.
I had to drop out of school temporarily because it was so bad.
I couldn’t read. I had trouble writing. And my memory was impaired.
I walked around all day with a cloud over my head.
But since then, I’ve learned that there are a number of ways to overcome brain fog, and you can implement them so that brain fog doesn’t slow you down and chip away at your quality of life.
Below are 20 steps that will help you clear away brain fog and regain your mental clarity.
What Is Brain Fog and What Causes It?
Researchers describe brain fog symptoms as “an interaction of physiological, cognitive, and perceptual factors” (1).
People suffering from brain fog describe it as feeling “forgetful,” “cloudy,” and “difficulty focusing, thinking and communicating” (2).
Brain fog symptoms are actually quite common, but that doesn’t mean they are normal and you should accept them. They are an important sign that something is wrong.
Brain fog can be caused by a number of things, including medication, poor diet, too much exercise, not enough sleep.
But the underlying mechanism is usually the same – inflammation.
Datis Kharrazian, author of the book Why Isn’t My Brain Working?, says that brain fog is often a sign of underlying brain inflammation and oxidative stress, which slows down neuronal communication. A number of studies also demonstrate this (38, 39).
When you experience brain fog acutely, it’s because your body is experiencing an increase in inflammation and oxidative stress. If you experience persistent brain fog, it’s because your body is chronically inflamed. Chronic inflammation is also linked to a number of mental disorders, including depression and dementia.
So a lot of my recommendations focus on reducing your overall systemic inflammation and oxidative stress.
On top of this, you may also have lower levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) if you struggle with brain fog. NAD is an enzyme that can be found in every cell of your body, and it helps your cells properly utilize the energy you get from food. Without enough of it, your body and brain won't function optimally (6, 7).
Check out this article to learn how to increase NAD levels.
NAD levels decline as you get older, but they can also be depleted from eating foods that cause high blood sugar levels (3-5).
And that leads us to my first recommendation…
1. Limit Refined Carbohydrates
If you want to prevent brain fog, the first thing you should do is avoid processed food that contain refined carbohydrates (particularly flour and sugar) because they increase inflammation and cause blood sugar fluctuations.
Chronically elevated blood glucose leads to insulin resistance and diabetes, which have been linked to memory loss and Alzheimer’s disease. A lot of researchers and experts are discovering that dementia should actually be called Type 3 diabetes (9-11).
Following a low-glycemic, low-grain diet will not only help you control your blood sugar, but it will also reduce inflammation that contributes to brain fog.
You should try your best to avoid refined sugar. Breakfast cereals, fruit juice and sport drinks containing high-fructose corn syrup are your brain’s worst enemies.
2. Eat Healthy Sources of Carbohydrates Instead
Even though you should avoid refined carbohydrates and sugar, that doesn’t mean you should avoid all carbohydrates.
Going on a long-term low-carbohydrate diet can backfire and eventually increase your brain fog.
Aim to get your carbohydrates from starchy vegetables and fruits instead.
My Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health contains plenty of healthy options.
I make sure I eat a decent amount of carbs every day, usually from:
Yams
Squash
Potatoes
Carrots
Other root vegetables
Berries
Apples
Bananas
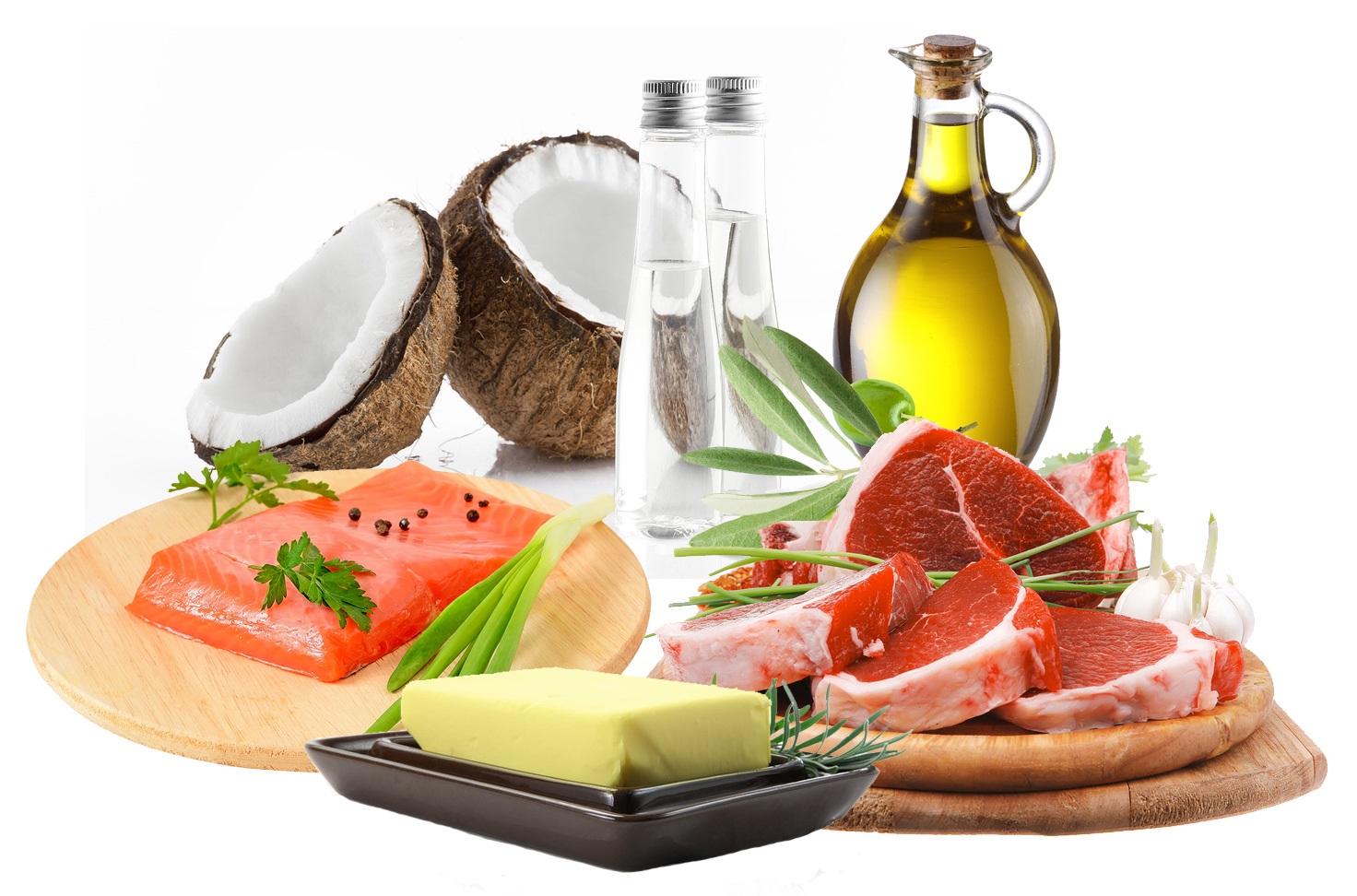
3. Eat Healthy Fats
Low-fat diets can be detrimental to brain health and contribute to your brain fog.
Your brain is mostly made up of fat and requires a steady supply of essentials fatty acids to run properly and smoothly (15).
The best sources of fat for your brain are:
Coconut oil
Olive oil
Salmon and krill oil
MCT oil
Avocado and its oil
Grass-fed beef
Egg yolks
Nuts and seeds
And you don’t need to worry about the cholesterol in these traditional foods. You brain depends on cholesterol. Too little of it actually increases your risk of mental illness and Alzheimer’s (62).
Furthermore, an imbalance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids can contribute to systemic inflammation. Today, most people get way too many inflammatory omega-6 fats from refined vegetable oils (corn, soybean, sunflower, safflower, canola). And they don’t get enough anti-inflammatory omega-3 fats from fatty fish, which are critical for optimal brain function.
So make sure you avoid vegetable oil, and eat enough wild salmon and grass-fed beef and/or supplement with krill oil. Doing so will reduce overall inflammation and brain fog symptoms over time.
4. Optimize Your Sleep and Circadian Rhythm
Not surprisingly, lack of high-quality sleep is one of the main causes of brain fog.
This is because poor sleep lowers your glutathione levels and increases oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain (40-43).
Disrupting your circadian rhythm also increases inflammation and oxidative stress (53-55).
This sleep supplement contains magnesium and a number of other natural compounds that I’ve used over the years to deepen sleep.
But I work with my clients so that they can maintain their circadian rhythm and maximize the quality of their sleep without so many supplements. We have free online workshop that talks about how you can work with us. You can register for the workshop here.
5. Support Methylation
Methylation is one of the most important processes in your body and brain.
It plays a role in the formation of almost all of your neurotransmitters, and methylation abnormalities often lie behind many brain and mental health problems (77).
Vitamins B6, B12 and folate are critical to the methylation process, and deficiencies can lead to poor methylation. So you can improve your methylation by making sure you get enough of them.
Optimal Energy includes the most bioavailable forms of B6 and B12, which I take every day. Every time I take it, I experience a boost in brain function and clarity.
I also take some extra folate a few times each week as I personally find I don’t need it every day.
Trimethylamine and SAM-e are two other critical nutrients in the methylation cycle that you could try to increase energy and mental clarity. I take them after drinking any alcohol.
6. B Vitamins
Besides supporting methylation, a number of the B vitamins have been shown to help combat brain fog.
Vitamin B1 helps turn glucose, the fuel for your brain, into energy. So brain fog and fatigue are often the first symptoms of vitamin B1 deficiency. Research shows that low levels of B1 are correlated with poor cognitive function in young adults, and even without a deficiency, supplementation with B1 leads to faster reaction times and reports of feeling more clear-headed (16, 17).
Vitamin B3 (niacin) is used by your body to form NAD, which I mentioned earlier is lower in people who struggle with brain fog.
Lastly, in my experience, vitamin B5 (pantethine) does a remarkably good job at clearing mental fogginess.
This supplement includes B1, B3 and B5.
It's also important to note that a number of psychiatric drugs have been shown to deplete B vitamins, and brain fog is a common side effect of these drugs. I've discussed this before. You can learn more here.
7. Increase Acetylcholine (Citicoline) and Dopamine (Tyrosine)
Another way to overcome your brain fog is by increasing production of acetylcholine and dopamine, two neurotransmitters that are critical for optimal brain function.
Acetylcholine is important for memory and learning, and dopamine increases mood, motivation and focus.
Citicoline (also known as CDP-Choline) is an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective nutrient that enhances the synthesis of acetylcholine and dopamine, and increases the number of acetylcholine and dopamine receptors in your brain. It also increases blood flow and mental energy in the frontal cortex of the brain, which is often compromised in people who suffer from chronic brain fog (80-85).
If that’s not enough, Citicoline has also been shown to improve cognitive speed and attention in young adults, stoke patients and elderly individuals with dementia (86-88).
Citicoline is the most bioavailable form of choline, an essential nutrient that most people don’t consume enough of because very few foods in the Western diet contain it. That’s why I recommend supplementing with it. It's included in the Optimal Brain supplement.
You can also find some choline in beef liver and egg yolks. That's why I'm a big fan of eating these foods regularly.
Unfortunately, many prescription drugs are anticholinergic, meaning they reduce acetylcholine in the brain.
The commonly-prescribed antidepressant Wellbutrin is anticholinergic, meaning it inhibits the physiological action of acetylcholine. I took it for multiple years, and I experience gradual cognitive decline during that time.
Once I got off Wellbutrin, I started supplementing with Citicoline and noticed a remarkable improvement in cognitive function since it increased my levels of acetylcholine and dopamine. I still take it today to help clear brain fog.
Make sure you read this article to learn more about the remarkable benefits of Citicoline.
Tyrosine also increases the production of dopamine.
It is an amino acid and precursor to dopamine.
Coffee and stimulants increase dopamine in the brain. So if you rely on them to get through the day, you likely have low dopamine, and increasing your natural production by supplementing with tyrosine may help you overcome brain fog.
I don’t take it regularly anymore, but tyrosine gives my brain a huge boost when I need it. I still use it sometimes, particularly if I don’t get enough sleep. It's also helpful for depression.
You should take tyrosine with vitamin B6 and vitamin C, as they are also cofactors in the production of dopamine.
Check out this article for more ways to increase dopamine. And this article for more ways to increase acetylcholine.
8. Limit Pharmaceutical and Recreational Drugs
A number of different pharmaceuticals and over-the-counter drugs cause brain fog and forgetfulness as side effects, including:
Anticholinergics
Antibiotics
Antihistamines
Blood pressure medication
Benzodiazepines are probably the worst for brain fog, as they’ve been linked to cognitive impairment and the development of dementia (79). I regret ever taking them for anxiety and sleep. Along with antidepressants, they caused me serious brain fog and cognitive impairment. Withdrawal from these medications can also cause brain fog.
Anticholinergic medications block acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter for learning and memory. There are more than 100 drugs that fall into the anticholinergic category. So if you’re taking an anticholinergic drug, make sure to take a choline supplement. The Optimal Brain supplement includes two high-quality sources of choline (78).
But it’s not just pharmaceutical drugs that can be a problem.
Not surprisingly, alcohol is also known to increase inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, and also lower NAD levels, so you should avoid it as much as possible to prevent brain fog (56-60).
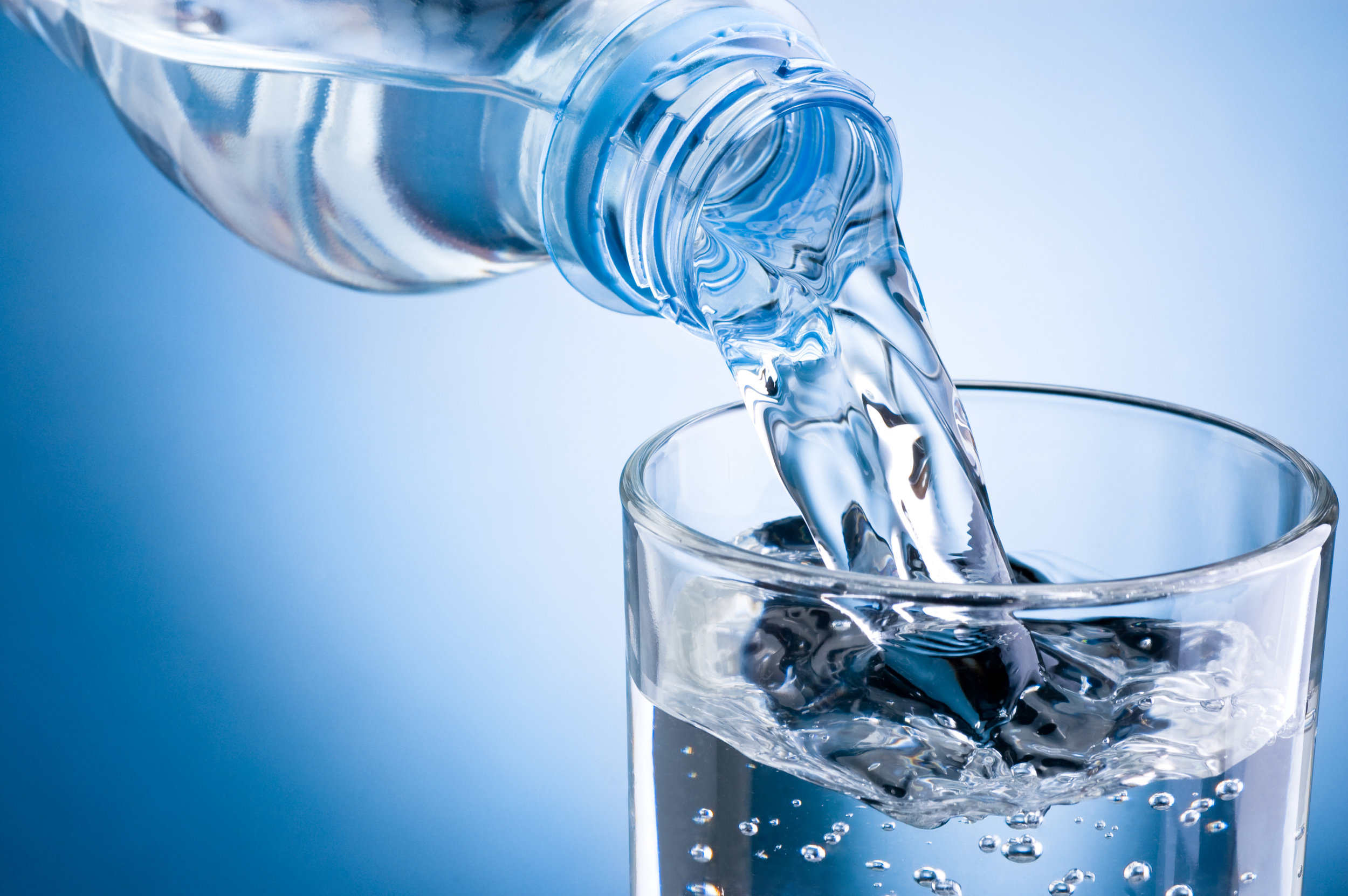
9. Hydrate with Clean Water
Your brain is 75% water by volume, so it makes sense that dehydration could cause brain fog (72).
Being dehydrated by just 2% has been shown to impair performance in tasks that require attention, psychomotor, and immediate memory skills (73).
But you also want to make sure you’re drinking the purest water possible. Otherwise, the water itself could be contributing to your brain fog.
Tap water contains fluoride and copper that could be contributing to your inflammation and brain fog.
There are also hundreds of other compounds in tap water, including trace amounts of pharmaceutical medication, which can affect your brain function.
I use a water filter to make sure I’m drinking the purest water available. It filters everything out of the water.
10. Elimination Diet
A study published in the Journal of Biological Psychiatry showed that food allergies and sensitivities could trigger a number of mental symptoms, including severe mental blankness and loss of motivation. Wheat, milk and eggs produced the most severe mental reactions (37).
If you struggle from brain fog (or any mental illness), you should eliminate the most common food allergens from your diet for at least two weeks, and then add them back in one by one and see how you feel:
Wheat, spelt, rye, barley, oats (gluten)
All dairy (casein, lactose)
Eggs
Soy
Corn
Nightshade vegetables
Nuts
Yeast
Shellfish
If cutting out all those foods seems overwhelming, start by eliminating all flour and gluten grains, including bread, cereal and pasta, and see how you feel. Don’t eat gluten-free junk food instead, as they are full of sugar and just as bad for brain fog.
Dr. Kenneth Fine, a pioneer in gluten intolerance research, has demonstrated that 1 in 3 Americans are gluten intolerant, and that 8 in 10 have the genes that predispose them to developing gluten intolerance. And research has also shown that gluten can contribute to ADHD, cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s (74-76).
Unfortunately, when you are gluten intolerant, you will often “cross-react” with other proteins similar to gluten. Plus, there are many other proteins in wheat other than gluten that can cause brain fog.
A lot of people who suffer from brain and mental health problems are also allergic or sensitive to lactose or milk protein (casein), which cause inflammation in the body and brain. So you should avoid all milk, cheese and yogurt, especially when you're trying to overcome brain fog.
I will never eat wheat and dairy again in my life. It’s just not worth it because my mood, energy and mental clarity are remarkably more consistent when I avoid them. I’m also intolerant to egg whites. I have to throw them away and only eat the yolks.
11. Forskolin
Forskolin is an active compound found in the roots of the Indian coleus (Coleus forskohlii).
It has been used by traditional cultures to treat various conditions and diseases (67).
I notice it increases mental energy and clarity for me.
This is because forskolin increases cyclic AMP (cAMP), which lowers inflammation (61).
12. Get Sun and Vitamin D3
I’ve discussed Vitamin D many times before, so I won’t belabor the point too much here.
But Vitamin D significantly affects your brain function, and turns on genes that support the production and release of dopamine and serotonin.
Yet most people are deficient (an estimated one billion people worldwide), and being low in Vitamin D can lead to chronic brain fog, low energy, poor memory, and depression (19).
It’s worth getting your levels checked and supplementing with it if you’re low.
Vitamin D levels above 40 ng/mL (100 nmol/L) reduce the risk of cognitive impairment, and low vitamin D levels are linked to higher risk of dementia (20).
Most people need to take at least 2000IU every day. I take 5000IU of this supplemental source of Vitamin D every day.
Using a Vitamin D lamp and getting enough sunlight can also help you with brain fog as they decrease inflammation (52).
It's important to test and monitor your Vitamin D levels before and after supplementing with it.
13. Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR)
Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR) is a neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing amino acid.
It is often used as a brain booster because it increases alertness and provides support to brain cells. It’s also been shown to be very effective at alleviating neurological decline and chronic fatigue (68-71).
I personally find ALCAR gives me a huge boost in brain energy and clarity. That's why it's included in the Optimal Brain supplement.
And as I discussed previously, it can protect your brain from alcohol.
Make sure you read this article to learn more about the remarkable benefits of ALCAR.
14. Exercise Properly
I’ve already discussed how exercise increases your brain’s growth hormone (brain-derived neurotrophic factor).
But it also reduces foggy thinking by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, improving blood flow to the brain, controlling blood sugar, and raising NAD levels (12).
But it’s important to note that chronic endurance exercise can actually increase inflammation, so be careful (13, 14).
That’s why I'm convinced that walking, weightlifting and sprinting are the best forms of exercise.
Overtraining and lack of rest will lead to hormonal imbalances and brain fatigue.
So when you engage in endurance cardio, make sure you don’t overexert yourself and always take long enough breaks between workouts to recover. Otherwise, you can physically and mentally exhaust yourself.
15. Increase Good Gut Bacteria
I’ve discussed this before, so I won’t go too in-depth here.
But there are approximately 100 trillion microorganisms and 500 known bacterial species living inside of you. Your digestive tract holds a lot of these bacteria, and cutting-edge research suggests there is a connection between your brain and your gut. Therefore, the makeup of these bacteria in your gut can affect how you feel mentally (50-52).
Unfortunately, a lot of people today have out-of-balance and dysregulated gut bacteria, which can increase inflammation and oxidative stress in the gut and brain, leading to brain fog and other mental symptoms.
Not surprisingly, research has shown that people with irritable bowel syndrome often have chronic fatigue syndrome. This is because both conditions often result from bacterial imbalances and gut inflammation (48).
Here are some steps I recommend to improve the composition of your gut bacteria, which can help eliminate symptoms of brain fog:
Take a high-quality probiotic.
Eat prebiotics foods – such as sweet potatoes, carrots, onions, asparagus, squash and others found in my free food guide – to promote the growth of good bacteria
Supplement with resistant starch
Avoid antibiotics unless absolutely necessary
Overall, you need a healthy gut for a healthy brain. You can read my previous article “5 Ways to Increase Your Good Gut Bacteria for a Healthier Brain” for more tips and information.
16. Take Adaptogens (Rhodiola, Ginseng)
Adaptogenic herbs help normalize the body and help you reach a state of mental balance (21, 22, 23).
I’ve weaned off psychiatric medications more than once. The very last time I did, I used two adaptogens – rhodiola and ginseng – and I noticed they reduced withdrawal symptoms, including brain fog.
Many studies show that rhodiola can clear brain fog and improve mental function by increasing cognitive energy and improving connections and communication between brain cells. It’s also been shown to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, which is linked to brain fog (24-29).
I wrote about rhodiola before if you’re interested in learning more.
I still use both rhodiola and ginseng regularly, especially if I’m dealing with brain fog for some reason.
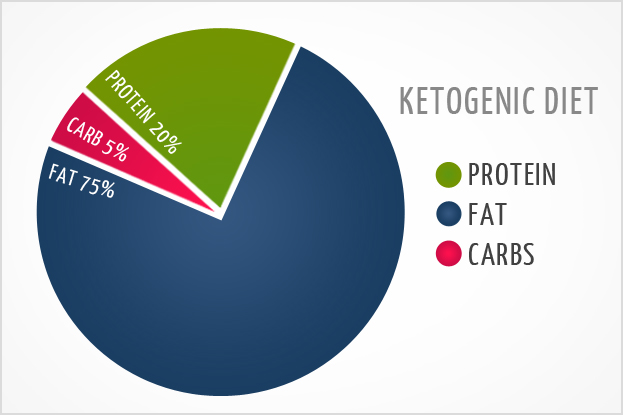
17. Intermittent Fasting and Ketosis
Short-term fasting and ketogenic dieting are great ways to enhance your mental clarity and reduce brain fog.
I fast for at least 12 hours every day, and sometimes follow a ketogenic diet to improve my cognition.
A ketogenic diet is a very low-carb diet. When there is limited access to carbohydrates, the body’s main source of energy, your body enters ketosis – a metabolic state in which your body and brain run on fatty acids and ketones. Ketones are an alternative source of fuel, which can quickly recharge your brain cells and improve cognitive function. (33).
This advice clearly contradicts my earlier advice that you should be eating plenty of healthy carbohydrates.
But some people notice their brain fog completely disappears and their cognition is very sharp if they fast or follow a low-carb ketogenic diet. But it’s not for everyone. Others feel much worse and need to eat enough carbs to feel mentally well. So I suggest you experiment with both and see what works for you.
You can get into ketosis more quickly by taking this supplement, which includes exogenous ketones that are easily digested by the body. They readily cross the blood-brain barrier, and provide instant energy to brain cells, helping you quickly overcome brain fog (30, 31).
18. Low-level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is about as cutting-edge as it gets. It’s even more unconventional that neurofeedback. And it works.
Low-level laser therapy, or photobiomodulation, is a treatment that uses low-level (low-power) lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to stimulate brain cells, helping them heal and function better (63).
LLLT increases blood flow to the brain and appears to have an effect on damaged brain cells, which can produce clearer, sharper thinking. It's important to note that the brain and mental effects of LLLT are limited to a specified set of wavelengths (18, 64, 65).
Most doctors are clueless about LLLT; but not every doctor.
Dr. Norman Doige, a physician who teaches at the University of Toronto here in Canada, discusses the amazing healing effects of LLLT in his book The Brain’s Way of Healing.
I first tried LLLT with a practitioner. I noticed a boost in cognitive energy, brain function and mental clarity.
I now use these devices at home:
Optimal 1000 Brain Photobiomodulation Therapy Light (Combo Red/NIR) - This is a powerful device that shines 660 nm of red light and 850 nm of infrared light. I shine it on my forehead for 5 minutes every day. I also shine it on other parts of my head and on my entire body, including on my thyroid, thymus gland and gut. I experience incredible benefits from doing this.
Vielight Neuro Duo – This is a transcranial-intranasal headset with 810 nm of near infrared light that I’ve now been using regularly. It penetrates deeper into brain tissue and is absorbed better by the central nervous system. If you decide to get this one, you can use the coupon code JORDANFALLIS for a 10% discount. Some research has shown a 20-fold higher efficiency of light delivery to the deep brain through the nose instead of transcranial application (125).
In my experience, applying the light directly to your forehead (prefrontal cortex) will help with brain fog.
This may seem strange and dangerous, but don’t worry – LLLT is very safe (66).
You can read about my experience with LLLT here.
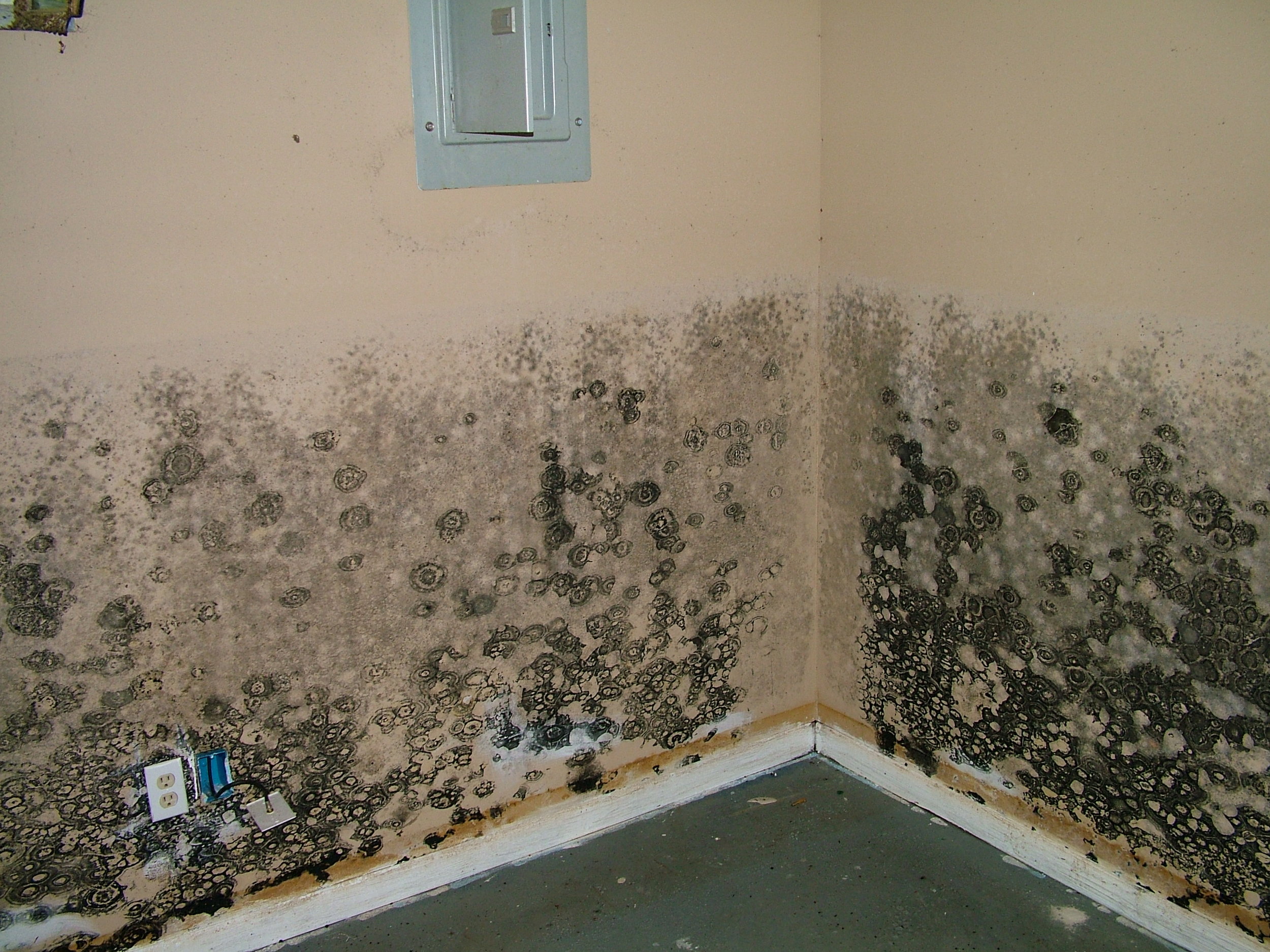
19. Avoid Environmental Mold and Mycotoxins
Environmental mold is a silent killer, as most people aren’t aware that it’s in their home and workplace and affecting their brain function. If you’re genetically susceptible, it can wreak havoc on your brain, and your cognitive abilities and mental health can deteriorate for no apparent reason.
After I lived in a moldy home, I became extremely sensitive to any environmental mold and mycotoxins (toxic metabolites produced by mold).
I now use an air filter in my apartment. It removes any mold spores and smoke that may be in the air.
Low amounts of mycotoxins are often found in some seemingly healthy foods, such as tea, nuts, coffee and chocolate. So if you’re sensitive to mycotoxins like I am, you’ll likely experience brain fog and fatigue after eating low-quality versions of these foods. I recommend finding the freshest, highest-quality, organic versions of these foods.
Lastly, if exposed to mold or their toxins, I supplement with activated charcoal or bentonite clay.
Activated charcoal and bentonite clay are potent natural treatments that can trap toxins and chemicals, allowing them to be flushed out of your body.
I take activated charcoal every time I eat something bad for my brain and mental health (mycotoxins, gluten, dairy), as it binds to problematic proteins and drags them out of my body. I notice I don’t feel as sick when I do this, and recover much more quickly than without it.
This is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to toxic mold. I’ll be writing more about it soon.
20. Increase Testosterone
This one applies to men only.
Low testosterone levels can contribute to your brain fog.
When I lived in a moldy home and suffered multiple concussions, my testosterone plummeted.
No conventional doctor tested my testosterone because they assumed every 20-year-old man would have healthy levels.
But they were wrong.
Eventually I saw an integrative physical and he found out that I had the testosterone levels of an old man.
I was put on testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) for almost one year to get my levels back to normal. And over that time, I saw a huge increase in my mental sharpness. I’m now off TRT and my testosterone remains at optimal levels because of my healthy lifestyle.
I recommend getting your levels checked and then consider TRT if necessary, especially when you’re older.
Your doctor will test your total testosterone levels. But it’s just as important to also check you free testosterone levels.
You can test your total and free levels here.
Conclusion
Clearly, there are a lot of causes and solutions to brain fog.
You don’t need to accept it as “normal.”
You may need to try a combination of these methods, and it may take some time to finally get to the bottom of it. But it can be done. And you can experience mental clarity again.
If you’re looking for an all-in-one solution to manage and overcome brain fog, check out the Optimal Energy supplement.
Do you struggle with brain fog? What helps you manage it? Have you overcome it for good?
Let me know in the comments, as your personal experiences could help someone.
References
(1) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23576989
(2) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23999934
(3) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22848760
(4) http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/53/11/2931.full
(5) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11939620
(6) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18493620
(7) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18165311
(8) http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=56589
(9) https://pubs.acs.org/cen/science/87/8720sci1.html
(10) http://www.neurology.org/content/early/2013/10/23/01.wnl.0000435561.00234.ee.short
(11) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2769828/
(12) http://jcb.rupress.org/conthttp://jcb.rupr
(13) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3793976/
(14) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23258605
(15) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20329590
(16) http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02246104#page-1
(17) http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s002130050163
(18) http://www.research.vahttp
(19) http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra070553
(20) https://www.vitamindcouncil.org/health-conditions/cognitive-impairment/
(21) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10468649
(22) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17504218
(23) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19601854
(24) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20378318
(25) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19168123
(26) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7756969
(27) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20378318
(28) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25172797
(29) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11410073
(30) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2604900/
(31) http://www.nutritionjrnl.com/article/S0899-9007(12)00365-6/abstract
(32) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15123336
(33) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17332207
(34) http://journals.plos.org/plospathogens/article?id=10.1371/journal.ppat.1003726
(35) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166432814004768
(36) http://www.pnas.org/content/108/38/16050.long
(37) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7225473
(38) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4490655/
(39) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3907532/
(40) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/09/080902075211.htm
(41) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24080377
(42) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1087079202902613
(43) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9760133
(44) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3497293/
(45) http://www.jimmunol.org/content/167/11/6518.full.pdf
(46) http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/35/10/2076.short
(48) http://nutritionandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1743-7075-7-79
(49) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002432050700358X
(50) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20357926
(51) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24669208
(52) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21412260
(53) http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/24202171/
(54) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16855156
(55) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23198849
(56) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20357926
(57) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24669208
(58) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3484320/
(59) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6407471
(60) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002432050700358X
(61) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17397885
(62) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15911792
(63) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2442599/
(64) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3953713/
(65) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3065857/
(66) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23675984
(67) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17345261
(68) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17658628
(69) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18065594
(70) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17693145
(71) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15039515
(72) http://www.nature.com/ejcn/journal/v57/n2s/full/1601898a.html
(73) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22855911
(74) http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2006/10/061010022602.htm
(75) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3184556/
(76) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/apt.12809/full
(77) http://ispub.com/IJNW/2/1/4476
(78) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18510583
(79) http://www.bmj.com/content/352/bmj.i90
(80) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2695184/
(81) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11796739
(82) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1430829/
(83) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1839138
(84) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1098982
(85) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19351232
(86) http://www.scirp.org/journal/PaperInformation.aspx?paperID=19921
(87) http://kyowa-usa.com/news/2014/07-29